What Is The Purpose Of The Nucleus In An Animal Cell
The nucleus is a pivotal organelle responsible for regulating almost all forms of cellular activities. Mostly, every type of cell that exists is categorized on the footing of the absenteeism or presence of the nucleus within its cell (categorized either as a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell.)
Tabular array of Contents
- Nucleus
- Structure
- Functions
- Important Questions

What is a Nucleus?
The most integral component of the cell is the nucleus (plural: nuclei). It is derived from a Latin give-and-take which means "kernel of a nut".
Nucleus Definition:
A nucleus is defined every bit a double-membraned eukaryotic prison cell organelle that contains the genetic material.
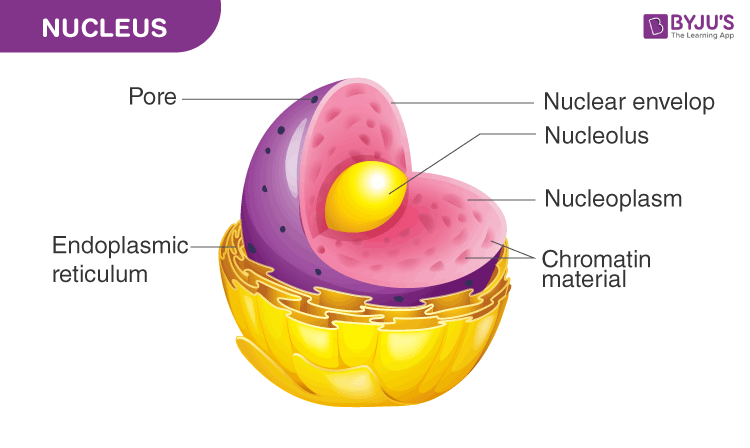
A nucleus diagram highlighting the various components. Moreover, merely eukaryotes have the nucleus, prokaryotes take the nucleoid
Equally stated above, the nucleus is institute only in eukaryotes and is the defining characteristic feature of eukaryotic cells. However, some cells, such equally RBCs exercise not possess a nucleus, though they originate from a eukaryotic organisms.
More to Explore: Difference Between Nucleus and Nucleoid
Structure Of Nucleus
- Typically, it is the nearly evident organelle in the cell.
- The nucleus is completely spring past membranes.
- It is engirdled by a construction referred to as the nuclear envelope.
- The membrane distinguishes the cytoplasm from the contents of the nucleus
- The jail cell'due south chromosomes are too confined within it.
- Dna is present in the Chromosomes, and they provide the genetic information required for the creation of different cell components in add-on to the reproduction of life.
Also Read:Nucleolus
Nucleus Office
Following are the important nucleus function:
- It contains the cell's hereditary information and controls the jail cell'south growth and reproduction.
- The nucleus has been conspicuously explained as a membrane-bound structure that comprises the genetic textile of a cell.
- It is not just a storage compartment for DNA, but too happens to exist the home of some important cellular processes.
- First and foremost, it is possible to duplicate one'south DNA in the nucleus. This process has been named DNA Replication and produces an identical re-create of the Dna.
- Producing two identical copies of the trunk or host is the start stride in cell division, where every new cell will get its ain set of instructions.
- Secondly, the nucleus is the site of transcription. Transcription creates unlike types of RNA from Dna. Transcription would exist a lot like creating copies of individual pages of the human body's instructions which may be moved out and read by the rest of the cell.
- The central rule of biology states that Dna is copied into RNA, and then proteins.
Also Read: Nuclear membrane
Detect more virtually the Nucleus, its features and functions, or any other related topics by registering at BYJU'South Biological science.
Further Reading:
- Plant cell
- Animal Cell
- Eukaryotic Cells
- Deviation betwixt Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Often Asked Questions
What is the nucleus?
The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle that contains the genetic cloth and other instructions required for cellular processes. Information technology is exclusively institute in eukaryotic cells and is besides one of the largest organelles.
Outline the structure of the Nucleus.
- A double-membraned organelle known as the nuclear membrane/envelope engirdles the nucleus.
- The nucleolus is found within the nucleus, occupying 25% per cent of the volume.
- Thread-like, dumbo structures known as chromatins are institute within the nucleus containing proteins and DNA.
- The mechanical strength for the nucleus is provided past the nuclear matrix, a network of fibres and filaments which performs functions similar to the cytoskeleton.
Highlight the functions of the nucleus.
The nucleus has ii primary functions:
- It is responsible for storing the cell's hereditary material or the DNA.
- Information technology is responsible for coordinating many of the important cellular activities such as protein synthesis, cell segmentation, growth and a host of other important functions.
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/the-nucleus/
Posted by: stewartfaturaved.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is The Purpose Of The Nucleus In An Animal Cell"
Post a Comment